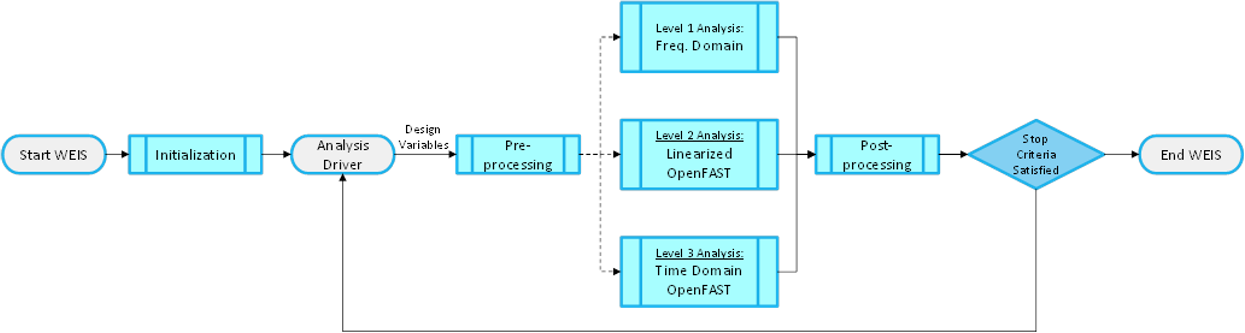
How WEIS works¶
WEIS is a stack of software that can be used for floating wind turbine design and analysis. The turbine’s components (blade, tower, platform, mooring, and more) are parameterized in a geometry input. The system engineering tool WISDEM determines component masses, costs, and engineering parameters that can be used to determine modeling inputs. A variety of pre-processing tools are used to convert these system engineering models into simulation models.
The modeling_options.yaml determines how the turbine is simulated. We currently support OpenFAST and RAFT.
The analysis_options.yaml determine how to run simulations, either a single run for analysis, a sweep or design of experiments, or an optimization.
A full description of the inputs can be found here (will point to rst when available).
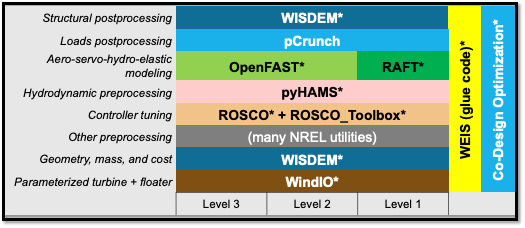
WEIS is “glued” together using openmdao components and groups.
- WEIS works best by running examples:
01_aeroelasticse can be used to set up batches of aeroelastic simulations in OpenFAST
02_control_opt can be used to run WEIS from an existing OpenFAST model, and optimize control parameters only
03_NREL5MW_OC3 and 04_NREL5MW_OC4_semi can be used to simulate the OC spar and semi, respectively, from WISDEM geometries.
05_IEA-3.4-130-RWT runs the design load cases (DLCs) for the fixed-bottom IEA-3.4 turbine
06_IEA-15-240-RWT contains several examples for running the IEA-15MW with the VolturnUS platform, including tower and structural controller optimization routines
15_RAFT_Studies contains an example for optimizing a the IEA-15MW with the VolturnUS platform in RAFT
More documentation specific to these examples can be found there, with more to follow.
This documentation only covers a summary of WEIS’s functionality. WEIS can be adapted to solve a wide variety of problems. If you have questions or would like to discuss WEIS’s functionality further, please email dzalkind (at) nrel (dot) gov.